A file format developed by Microsoft and IBM to represent audio.
It is also known as a WAV files due to its .wav suffix.
WAV is a specialized form of the Resource Interchange File Format.
Utility
Old as the format may be, it still is a popular format for the following reasons:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Simplicity | The structure of the format is relatively easy to understand by humans, and subsequently decoded by a program |
| Portability | This format is considered standard by many software and hardware platforms |
| High fidelity | Stores the audio data raw, uncompressed, thereby retaining the highest quality. Unlike MP3. |
File Structure
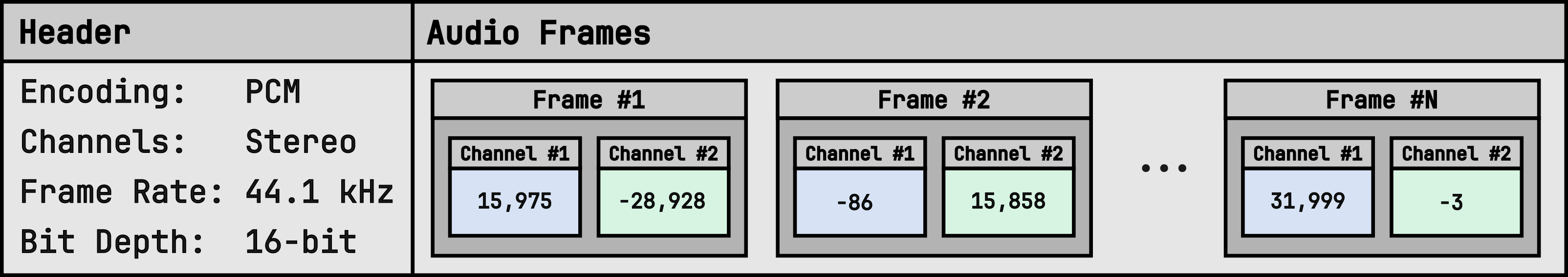
A WAV file consists of the header along with individual audio frames storing the amplitudes for each channel (left-right or rear-back).
Header
Describes the audio metadata and how the subsequent data should be interpreted.
| Keys | Description |
|---|---|
| Encoding | Digital representation of an audio sample |
| Channel | Describes the number of output channels (e.g. mono and stereo) |
| Frame Rate (a.k.a Sample Rate) | The number of frames in a second. Measured in Hertz. It affects the range of representable frequency, affecting sound quality perception. |
| Bit Depth | Affects the dynamic range of the audio. More bits means more fine-grained intervals of loudness can be represented. |
Note
The WAV file format expects the byte order of multi-byte values to be little-endian.